General Electric, with the assistance of the McKinsey and
Company consulting firm, developed a more complicated matrix. As depicted in Figure below, the GE Matrix includes nine cells based on
long-term industry attractiveness and business strength/competitive position.
The GE Matrix, in contrast to the BCG Growth-Share Matrix, includes much more
data in its two key factors than just business growth rate and comparable market
share. For example, at GE, industry
attractiveness includes market growth rate, industry profitability, size, and
practices, among other possible opportunities and threats. Business strength or competitive
position includes market share as well as technological position, profitability,
and size, among other possible strengths and weaknesses.
The individual product lines or business units are
identified by a letter and plotted as circles on the GE Business Screen. The area of each circle is in proportion
to the size of the industry in terms of sales. The pie slices within the circles
depict the market share of each product line or business unit.
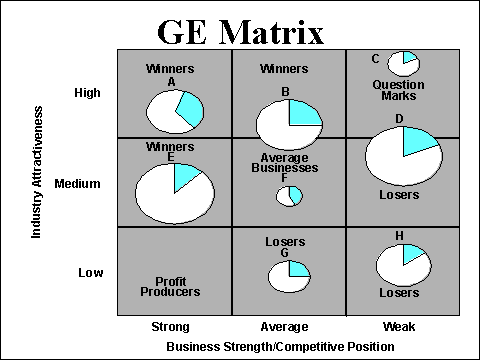
Figure:
The Industry Attractiveness-Business Strength Matrix

Dimensions of the Matrix
Industry
Subjective assessment based on external factors,
Attractiveness
noncontrollable by the firm, that are intended to capture the industry and
competitive structure in which the business operates.
Business
Subjective assessment based on the critical success Strength
factors, largely
controllable by the
firm, that define the
competitive position of a business within its industry.